Xanax vs Ativan
When comparing Xanax (alprazolam) vs Ativan (lorazepam), two commonly prescribed medications used to treat anxiety and panic disorders, several facts deserve your attention. First, pursuant to the National Center for Health Statistics, a sobering number of more than 11,500 lives were lost in 2017 due to benzodiazepine overdoses (the family of drugs these two anxiety drugs belong to). A chilling reminder of their risky potency. Yet, Xanax was a top prescribed drug in the last two-plus decades, with a whopping 25 million prescriptions filled in America alone, during 2009 to 2017 [1].
Here’s the twist: both drugs fight anxiety differently. Xanax works fast, bringing instant relief while, bam, Xanax knocks it out cold. But Xanax’s effects fade more swiftly, leaving patients craving more.
Ativan, on the other hand, lasts longer providing a slower, steady calming for hours. Which can offer a better, more constant anti-anxiety medication. Both have their downsides, though. Drowsiness, dizziness, confusion – side effects that can dance a clumsy jig across your day. Xanax, however, leans heavily on the sleepy side, a potential party-crasher for your to-do list.
As for addiction risks, both are addicitive. With prolonged use patients can find themselves with unwanted dependencies. But Xanax, with its rapid onset and shorter stay, is even more likely to create a dependence. So which is the better choice? Read on for more.
What is Ativan?
Ativan is used to relieve anxiety. Ativan is in a class of medications called benzodiazepines. It works by slowing activity in the brain to allow for relaxation. Ativan is also used to treat irritable bowel syndrome, epilepsy, insomnia, nausea, and vomiting from cancer treatment and to control agitation caused by alcohol withdrawal. [1]
The Ativan side effects may be habit-forming. Do not take a larger dose; take it more often or longer than your doctor tells you to. Tell your doctor if you have ever drunk large amounts of alcohol, if you use or have ever used street drugs, or have overused prescription medications. Do not drink alcohol or use street drugs during your treatment. Drinking alcohol or street drugs during your treatment with Ativan also increases the risk that you will experience these serious, life-threatening Ativan side effects. Also, tell your doctor if you have or have ever had depression or another mental illness.
What is Xanax?
Xanax dosages are used to treat anxiety disorders and panic disorder (sudden, unexpected attacks of extreme fear and worry about these attacks). Xanax is in a class of medications called benzodiazepines. It works by decreasing abnormal excitement in the brain.
Xanax may be habit-forming or cause drug addiction. Do not take a larger dose; take it more often or longer than your doctor tells you to. Tell your doctor if you have ever drunk large amounts of alcohol, if you use or have ever used street drugs, or have overused prescription medications.

Ativan vs Xanax – Similarities
Ativan (lorazepam) and Xanax (alprazolam) are both used to treat anxiety and other psychiatric disorders. They are in the benzodiazepine family of drugs, which help inhibit excess nerve stimulation in the brain.
Ativan vs Xanax – Differences
The differences are:
- Xanax has a quicker onset of effect but a shorter duration of action (4 to 6 hours) compared with Ativan’s 8 hours.
- Sedative and performance-impairing effects may occur sooner with Xanax but dissipate quicker than with Ativan.
- The activity of Xanax is more likely to be affected by race (people of Asian descent achieve higher concentrations, and activity of Xanax lasts longer), concurrent liver or kidney disease, alcoholism, and obesity. In contrast, Ativan is less likely to be influenced by race or age.
Ativan and Xanax are usually not prescribed together.
How do Ativan and Xanax Work?
Ativan and Xanax are both effective for anxiety and other psychological conditions and have similar side effects, warnings, and drug interactions. Consult your healthcare provider to see if one of these medications is appropriate for you and your condition.
Ativan vs Xanax – Which Drug is More Effective for Anxiety?
Ativan and Xanax are both benzodiazepines used for the treatment of anxiety, and both are effective for this use. A placebo-controlled, double-blind study compared Ativan and Xanax in the treatment of patients with severe anxiety. Both drugs were found to be more effective than placebo, with Xanax being slightly more effective in the later weeks of the study. However, another study of the two drugs for anxiety showed both drugs to be effective, with Ativan being slightly more effective. [2]
Another study compared the two drugs in the treatment of panic disorder and found Ativan and Xanax to be equally effective. The most effective medication for you should only be determined by your doctor, who will take into account your medical condition(s), history, and other medications you take.
Ativan and Xanax are both effective for anxiety and other psychological conditions and have similar side effects, warnings, and drug interactions. However, the drugs can be prescribed in different strengths which can make them more suitable for different situations and patients. Let’s look at a comparison table, citing studies and sources, to help you understand which drug might be more effective for your specific needs:
| Condition | Ativan (Lorazepam) | Xanax (Alprazolam) |
|---|---|---|
| Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) | – More effective in reducing GAD symptoms according to a Journal of Clinical Psychiatry study. (source: Journal of Clinical Psychiatry: psychiatry.org) | – Faster onset of action for immediate relief, but studies lack conclusive comparisons to Ativan’s effectiveness for long-term GAD management. (source: Drugs.com: drugs.com) |
| Panic Attacks | – Effective, but slower onset may limit immediate relief. | – Ideal for panic attacks due to rapid onset and potent anxiolytic effects. (source: American Journal of Psychiatry: ajp.psychiatryonline.org) |
| Onset and Duration | – Slower onset: takes 1-2 hours to kick in. | – Faster onset: works within 15-30 minutes. |
| Duration of Effects | – Longer-lasting: effects linger for 4-8 hours. | – Shorter duration: effects wear off in 3-6 hours. |
| Side Effects | – Drowsiness, dizziness, confusion. | – Similar to Ativan, but drowsiness may be more pronounced. |
| Dependency and Withdrawal Risk | – Both carry risk of dependence and withdrawal symptoms with prolonged use. | – Xanax, with its faster onset and shorter half-life, may have a higher potential for misuse and addiction. |
| Safety Concerns | – Safer for older adults or individuals with liver problems due to slower elimination and less reliance on liver metabolism. | – More prone to interactions with other medications, increasing risk of complications. (source: Mayo Clinic: mayoclinic.org) |
Which Drug is More Addictive?
Both Ativan and Xanax should only be used short-term due to the risk of drug addiction and dependence. Generally speaking, benzodiazepines with a shorter half-life (such as Ativan and Xanax) are harder to stop than those with a longer half-life (such as diazepam). Both Ativan and Xanax readily enter brain tissue which reinforces drug-taking and is generally associated with more severe withdrawal symptoms. Therefore, Ativan and Xanax are both at high risk of abuse. Research directly comparing Ativan with Xanax is not available; however, many experts have particularly advised that Xanax be used with caution as it has been associated with particularly severe benzo withdrawal symptoms.

Ativan vs Xanax for Sleep
Ativan and Xanax are both FDA-approved for anxiety relief and are less likely than some other benzodiazepines (such as diazepam or temazepam) to induce sleep. Sedative effects of Ativan that did occur were of slower onset but may last longer than Xanax. Ativan may also be used in the treatment of seizures.
Ativan vs Xanax – Which is Stronger?
It’s hard to categorize Ativan as milder or not; however, we do know that a dose of Xanax wears off faster than a dose of Ativan. Therefore, Xanax may be dosed more frequently than Ativan.
Ativan vs Xanax Withdrawal
The FDA has found that benzodiazepine drugs, such as Ativan and Xanax, when used in combination with opioid medications or other sedating medications can result in serious adverse reactions including slowed or difficult breathing and death. Patients taking opioids with benzodiazepines, other sedating medications, or alcohol, and caregivers of these patients, should seek immediate medical attention if that start to experience unusual dizziness or lightheadedness, extreme sleepiness, slow or difficulty breathing, or unresponsiveness.
As a benzodiazepine, both Xanax and Ativan come with the risk of abuse, misuse, and prescription drug addiction. The physical dependence on Ativan can occur with prolonged use of the medication. A withdrawal reaction may occur when stopping the use of the drug, but this risk can be reduced by slowly reducing the dose of Ativan when stopping.
Ativan vs Xanax Side Effects
Side effects of Ativan and Xanax tend to be greater at higher doses. The most common side effects of Ativan are sedation, dizziness, and weakness. Patients taking Xanax often experience sedation, dizziness, and weakness.
Other side effects that may occur with either drug include:
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness
- Drowsiness
- Amnesia/memory impairment
- Confusion
- Disorientation
- Depression
- Euphoria
- Suicidal ideation/attempt
- Incoordination
- Lack of energy
- Dry mouth
- Tremor
- Convulsions/seizures
- Vertigo
- Visual disturbance (double or blurred vision)
- Slurred speech
- Change in libido
- Impotence
- Decreased orgasm
- Headache
- Coma
- Respiratory depression
- Apnea/worsening of sleep apnea
- Worsening of obstructive pulmonary disease
- Gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms include nausea, constipation, or diarrhea
Other side effects may occur. Consult a healthcare professional for a complete list of side effects.
Which is Stronger Ativan or Xanax Infographic
There are a few things to consider when contrasting the two widely prescribed drugs used to treat anxiety and panic disorders, Ativan (lorazepam) and Xanax (alprazolam).

Embed the above “Which is Stronger Ativan or Xanax” Infographic to your Website. This infographic is provided by the We Level Up Addiction Treatment Center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://weleveluptx.com/ativan-vs-xanax/
Which is Stronger Ativan or Xanax image link: https://weleveluptx.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Which-is-Stronger-Ativan-or-Xanax-1024×1024.png
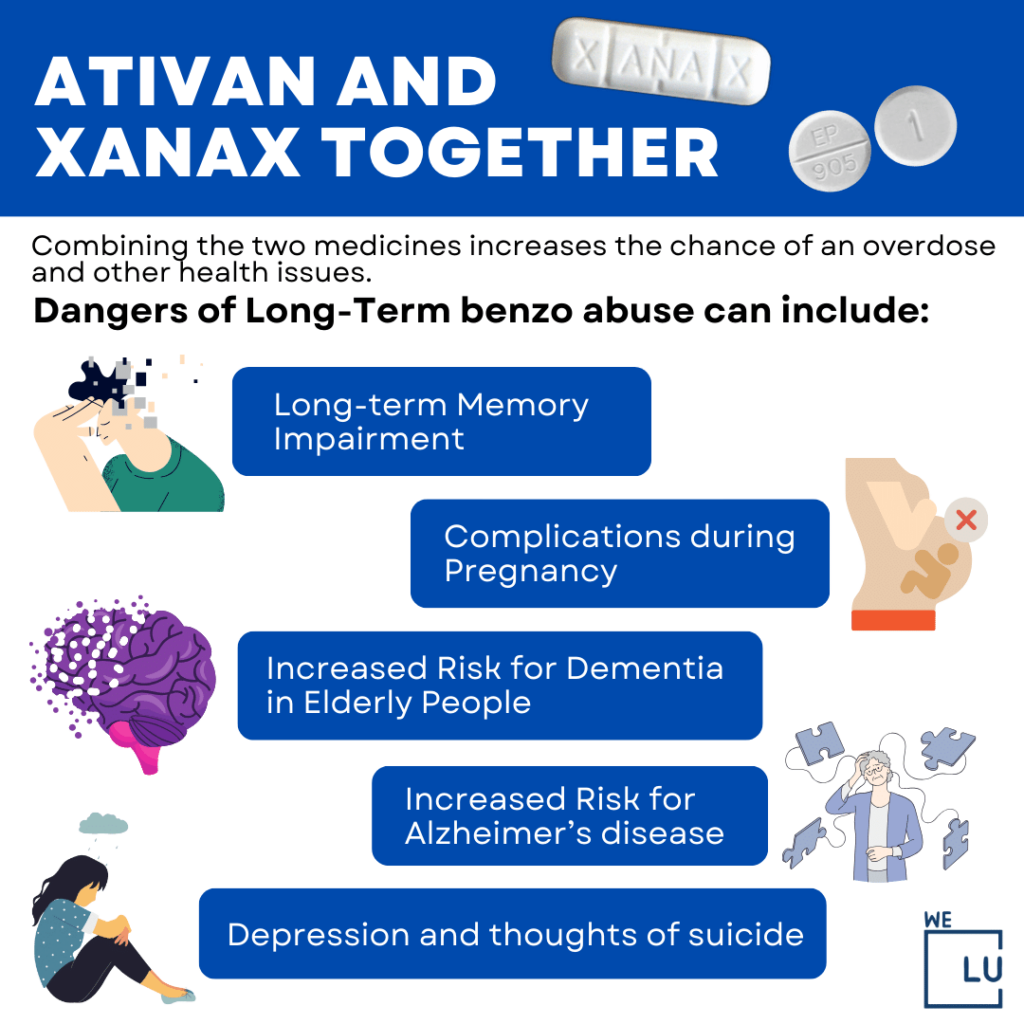
Embed the above “Ativan and Xanax Together” Infographic to your Website. This infographic is provided by the We Level Up Addiction Treatment Center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://weleveluptx.com/ativan-vs-xanax/
Ativan and Xanax Together image link: https://weleveluptx.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Ativan-and-Xanax-together-1024×1024.png
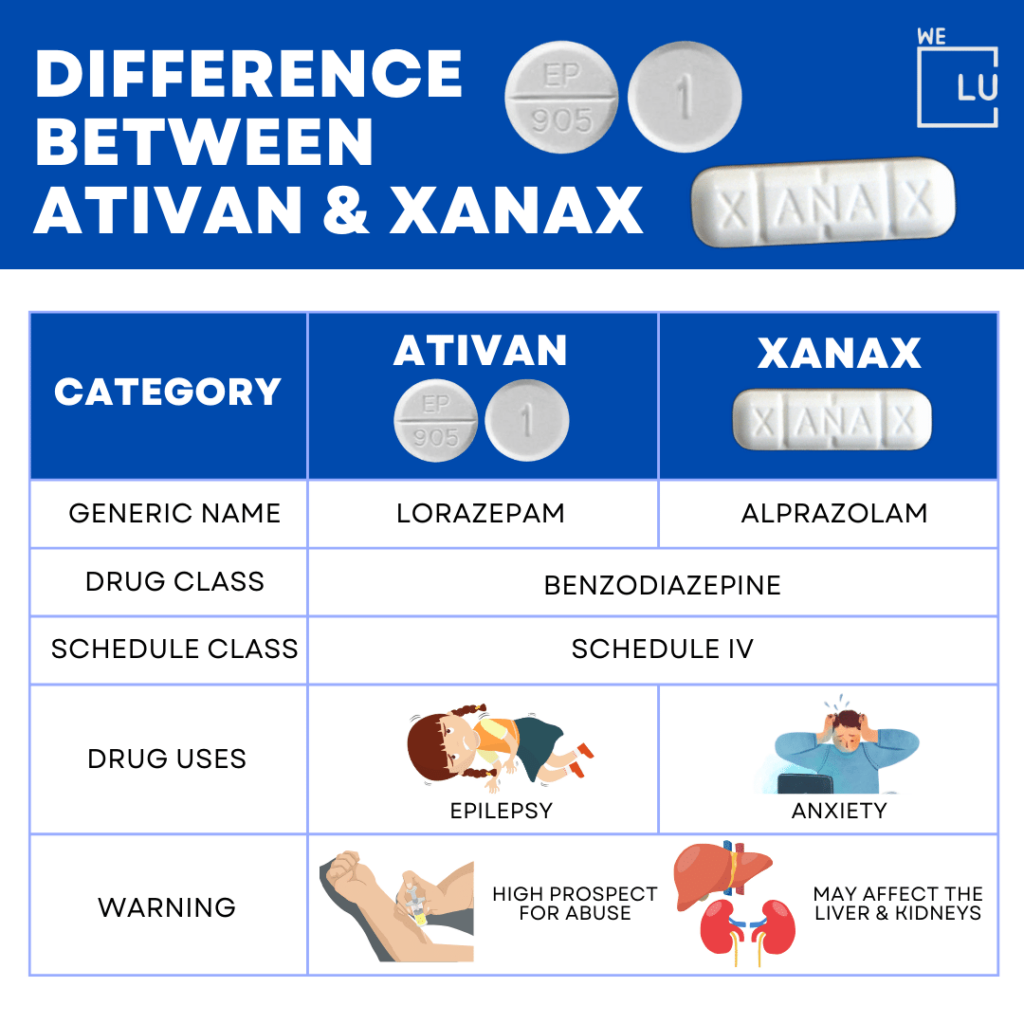
Embed the above “Difference between Ativan & Xanax” Infographic to your Website. This infographic is provided by the We Level Up Addiction Treatment Center team. To use the above infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://weleveluptx.com/ativan-vs-xanax/
Difference between Ativan & Xanax image link: https://weleveluptx.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Difference-between-Ativan-Xanax-1024×1024.png
Addiction Treatment & Inpatient Drug Rehab Texas
Mental health and substance use disorders affect people from all walks of life and all age groups. These illnesses are common, recurrent, and often serious, but they are treatable and many people do recover. Mental disorders involve changes in thinking, mood, and/or behavior. These disorders can affect how we relate to others and make choices. Reaching a level that can be formally diagnosed often depends on a reduction in a person’s ability to function as a result of the disorder. For example:
- Serious mental illness is defined by someone over 18 years old having (within the past year) a diagnosable mental, behavior, or emotional disorder that causes serious functional impairment that substantially interferes with or limits one or more major life activities.
- Substance use disorders occur when the recurrent use of alcohol and/or drugs causes clinically significant impairment, including health problems, disability, and failure to meet major responsibilities at work, school, or home. [3]

How We Can Help? Searched for “Texas inpatient consultants or drug and alcohol treatment centers in Houston TX?” or are you seeking a national inpatient rehab destination?
Receive detox and treatment for co-occurring disorders today.
As the addiction treatment community begins to realize that addiction is itself a mental disorder, the relationship between substance abuse and mental disorders becomes more complicated. The greater treatment community largely lacks a proper understanding of dually diagnosed conditions, so these conditions are still treated separately, or worse–not treated or diagnosed at all. The dual diagnosis treatment centers in We Level Up Florida, California, Texas, and New Jersey are some of the facilities that have professionals trained to help treat co-occurring disorders concurrently. This type of tandem treatment provides some of the best success rates.
Get dual diagnosis treatment for individuals struggling with Ativan vs Xanax or drug abuse. Call We Level Up TX today!
Sources:
[1] Alprazolam prescriptions number U.S. 2004-2021 | Statista Lorazepam – U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
[2] Long-term comparison of alprazolam, lorazepam, and placebo in patients with an anxiety disorder – National Center for Biotechnology Information
[3] Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders – Substance Abuse and Mental Health Service Administration