What is The Difference Between ADD vs ADHD?
ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) and ADD (attention deficit disorder) are often mistakenly interchanged, leading to confusion. ADHD is characterized by symptoms such as hyperactivity, impulsivity, and inattention. Conversely, ADD is an outdated term associated with a subtype of ADHD specifically characterized by inattention symptoms.
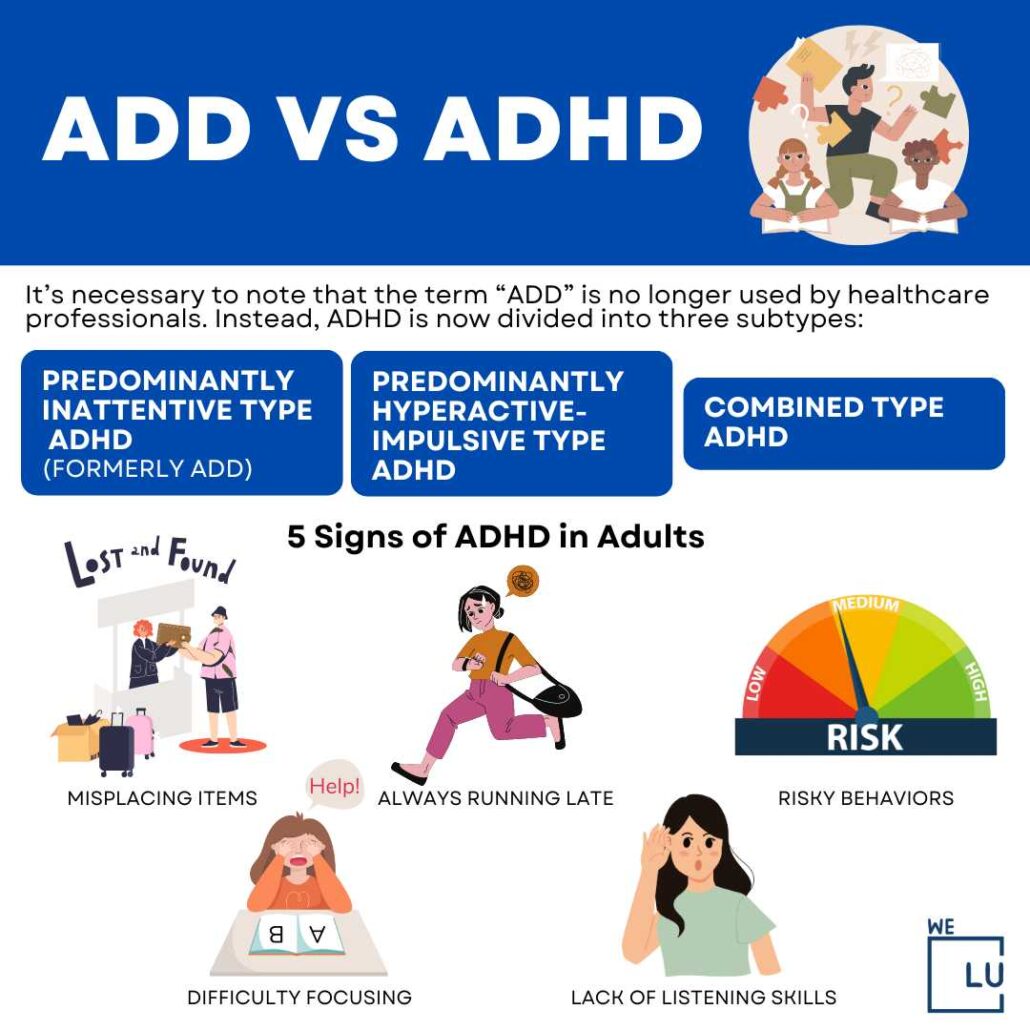
Healthcare professionals no longer use the term “ADD,” opting instead to categorize the condition into three distinct subtypes of ADHD. Each subtype reflects a unique set of symptoms and behavioral patterns.
Accurate diagnosis by a healthcare professional is crucial for receiving appropriate ADHD treatment. Delving into these subtypes provides valuable insights into how individuals’ attention and cognitive functions vary, enhancing our understanding of this neurodevelopmental condition.
Discover professional help from We Level Up’s addiction and mental health therapists. Start getting support with a free call to our addiction hotline.
ADD vs ADHD Adults Today
In our current comprehension, ADHD presents a more extensive range of symptoms than the formerly employed term ADD. While ADD predominantly focuses on challenges in maintaining attention, ADHD acknowledges both attention-related issues and hyperactivity-impulsivity components, providing a more inclusive depiction of the condition.
Predominantly Inattentive Type ADHD
The DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders) delineates diagnostic criteria for various mental conditions, encompassing ADHD (DSM 5 ADD vs ADHD). In cases of this specific ADHD subtype (previously termed ADD), DSM-5 notes the absence of hyperactivity symptoms; however, individuals may still display the following:
- Difficulty organizing tasks or activities.
- Easy distraction from assigned tasks.
- Frequent forgetfulness regarding daily activities.
- Persistent misplacement of necessary items for work.
- Aversion, dislike, or procrastination of uninteresting activities.
- Loss of concentration on projects, chores, or duties in the workplace or office.
- Difficulty following clear directions.
- Seeming inattentiveness during conversations.
- Frequent careless mistakes.
- Struggling to focus on tasks or social interactions.
Within the DSM-5’s comparison of ADD vs ADHD, ADHD incorporates both the inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive presentations, supplanting the erstwhile term ADD.
Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive Type ADHD
Individuals diagnosed with hyperactive-impulsive type ADHD exhibit the following indications:
- Consistently being in motion or “on the go.”
- Squirming in their seat, engaging in desk-related fidgeting, or tapping hands or feet.
- Frequently leaving their seat at inappropriate moments, such as during work meetings, classes, or presentations.
- Excessive talking.
- Difficulty waiting for their turn.
- Interrupting others in conversation or intruding on activities.
- Blurting out answers before a question is fully articulated.
ADHD Combined Type
Impulsive and hyperactive behaviors, alongside inattention and distractibility, characterize this prevalent form of ADHD. Moreover, the following criteria must be satisfied:
- Presence of several inattentive or hyperactive-impulsive symptoms.
- Manifestation of symptoms in two or more settings (e.g., at home, school, work, with friends or relatives, or in other activities).
- Clear evidence that these symptoms impede or diminish the quality of social, school, or work functioning.
- The symptoms are not better accounted for by other mental disorders, such as mood, anxiety, dissociative, or personality disorders. Additionally, the symptoms do not occur exclusively during schizophrenia or another psychotic disorder.
Understanding ADD vs ADHD Symptoms
While the diagnostic criteria remain consistent across age groups, adults may encounter distinct challenges in managing ADHD compared to children.
Adults with undiagnosed or untreated ADHD may grapple with issues related to work productivity, relationships, time management, or finances due to difficulties in concentration and organization. Adults diagnosed with either form of ADHD must receive appropriate treatment and support to manage their symptoms effectively.
While the signs and symptoms of ADHD and ADD in adults share similarities, there are notable differences. Individuals with ADHD may exhibit a higher tendency for impulsive behavior, procrastination, and risk-taking, whereas those with ADD may lean towards inattentiveness, spacing out, or easy distractibility. Individuals with ADD often struggle with sustained attention on tasks, while adults with ADHD may find transitioning between functions challenging.
Restlessness and difficulty staying still may be more prevalent in adults with ADHD, whereas those with ADD may experience a slower pace and encounter challenges initiating tasks. ADHD adults may struggle with active listening and following instructions, while individuals with ADD may face difficulties in organization, memory retention, and time management. Both scenarios can lead to disorganization, posing challenges in maintaining commitments to work, school, relationships, and household responsibilities.
ADHD vs ADD Diagnosis
ADHD is a clinically diagnosed disorder without specific laboratory or radiologic tests. Neuropsychological tests lack sensitivity for diagnosis, making the patient’s history the primary basis for diagnosis.
Evaluation typically involves various rating scales and input from multiple informants, such as teachers, guardians, and parents. Clinicians must rule out other disorders contributing to the symptoms, avoiding diagnoses within the context of conditions like psychotic or manic episodes.
ADHD encompasses combined, inattentive, and hyperactive-impulsive presentations, while ADD specifically pertains to the inattentive presentation. Both share a core feature of difficulty maintaining focus and sustained concentration.
To distinguish between ADHD and ADD, therapists analyze varying symptoms. ADHD is a prevalent neurodevelopmental disorder typically diagnosed in childhood, often persisting into adulthood. The official medical term for the condition is ADHD, irrespective of whether hyperactivity symptoms are present. ADD, an outdated term from the DSM-3, denotes inattentive-type ADHD, characterized by disorganization, lack of focus, and forgetfulness.
For adult cases of ADD vs ADHD, two subtypes were initially identified: ADD with hyperactivity and ADD without hyperactivity. However, in the 1987 revision by the American Psychiatric Association (APA), these subtypes were consolidated into a unified condition referred to as ADHD.

Finding Help For ADD and ADHD
Distinguishing between attention-deficit disorder (ADD) and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) can impact one’s ability to concentrate on academic tasks, engage in social interactions, and perform everyday activities such as dressing or working. Familiarize yourself with ADHD symptoms and explore available treatment options. Similar signs of ADD or ADHD may manifest in mood disorders, anxiety disorders, personality disorders, and dissociative disorders.
Engaging in mental health rehabilitation can be advantageous for addressing and navigating the difficulties linked to ADHD. This approach offers customized strategies and support, empowering individuals to enhance their well-being and functionality.

Skip To:
Learn More:
If you’re struggling with ADHD symptoms, get resources for treatment counseling that works. Start getting support with a free call to our mental health and addiction hotline.
Opening Soon! World-class, Accredited, Anticipated 5-Star Reviewed, Effective Addiction & Mental Health Programs. Complete Behavioral Health Inpatient Rehab, Detox plus Co-occuring Disorders Therapy.
FREE Addiction Hotline – Call 24/7End the Addiction Pain. End the Emotional Rollercoaster. Get Your Life Back. Start Drug, Alcohol & Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Treatment Now. Get Free No-obligation Guidance by Substance Abuse Specialists Who Understand Addiction & Mental Health Recovery & Know How to Help.
In-Depth ADD vs ADHD Differences
Concerning the distinction between ADD meaning and ADHD, the primary differentiation lies in the exhibited symptoms. ADD, also recognized as the inattentive subtype of ADHD, is characterized by challenges in sustaining attention and organizing tasks without the prominent presence of hyperactivity or impulsivity. In contrast, ADHD encompasses two primary subtypes: the predominantly inattentive presentation and the combined presentation, which includes both inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity.
From a neurological perspective, these differences in symptomatology are believed to arise from variations in brain activity, neurotransmitter levels, and connectivity patterns within the prefrontal cortex and other relevant brain regions.
Inattentive ADHD Symptoms
Inattentive ADHD is one of the three categories within the attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) diagnosis. Individuals with the inattentive type of ADHD often exhibit a quieter demeanor, frequent daydreaming, easy distractibility, forgetfulness, challenges in maintaining focus, and may appear disorganized. Treatment for inattentive ADHD involves lifestyle adjustments, medication, cognitive behavioral therapy, coping strategies, and access to supportive resources.
Common symptoms of inattentive ADHD in both women and men encompass:
- Difficulty paying attention.
- Ease of forgetting things.
- Need for assistance in completing tasks.
- Disorganization.
- Procrastination.
- Difficulty sustaining focus on a single activity for an extended period.
- Challenges in multitasking.
- Struggles with following through on commitments.
When considering ADD vs ADHD in females, there may be a tendency for more internalized symptoms, such as daydreaming or organizational difficulties, which might be easily overlooked compared to the more overt hyperactivity often observed in males. Recognizing and addressing ADHD symptoms in a gender-sensitive manner is crucial to understanding the diverse ways in which they may manifest in women and men.
Inattentive ADHD in Women
Females with inattentive ADHD may encounter distinctive symptoms, including challenges in managing relationships, emotions, and multitasking. Those with this ADHD subtype might struggle to recognize patterns, make intuitive leaps, and grapple with abstract ideas. Additionally, women with inattentive ADHD may contend with heightened daily stress, exacerbating their symptoms and rendering them more challenging to navigate. The treatment approach for inattentive ADHD in women often involves lifestyle adjustments.
The underdiagnosis of ADHD in adult women is common, given the variations in how symptoms manifest in females. Women with ADHD may experience heightened distraction compared to men, and the intrusive thinking associated with their ADHD might manifest more as rumination than impulsivity.
Primary ADHD and ADD Difference
Challenges in concentration, impulsivity, and hyperactivity define attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Attention deficit disorder (ADD) shares the difficulty with concentration but lacks the components of hyperactivity and impulsivity.
Since the introduction of the DSM-5 in 2013, both ADD and ADHD are now classified as subtypes of a unified condition.
ADD in Adult Men
ADHD in males is frequently marked by challenges sustaining focus, impulsive decision-making, and organization and time management difficulties.
Hyperactivity symptoms observed in childhood may transform into a sense of restlessness or inner agitation in adulthood, impacting multiple facets of life, including work, relationships, and overall well-being.
In adult males, ADHD may manifest through the following signs and symptoms:
- Difficulty sustaining attention, hindering task focus.
- Impulsivity results in hasty decisions and self-regulation challenges.
- Organizational difficulties affecting time management and task completion.
- Restlessness or inner agitation.
- Inconsistent performance and frequent procrastination.
- Relationship challenges due to communication and attentiveness issues.
- Elevated risk of developing comorbid conditions like anxiety and depression.
- Adoption of coping mechanisms such as excessive caffeine consumption or engaging in high-risk behaviors.
- Varied employment history stemming from struggles with maintaining consistent work performance.
- Challenges in managing personal finances and responsibilities.
Accurate diagnosis and tailored interventions for ADHD in adult males hinge on a thorough understanding of these distinctive characteristics.
ADHD Pathophysiology
ADHD is linked to cognitive and functional impairments associated with widespread abnormalities in the brain. Individuals with ADHD exhibit smaller anterior cingulate gyrus and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLFPC), contributing to deficits in goal-directed behavior. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) also indicates reduced activity in the frontostriatal region. A comprehensive understanding of these pathophysiological mechanisms is crucial for directing treatment interventions effectively.
ADD vs ADHD Fact Sheet
ADHD Meaning
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition marked by enduring patterns of inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity surpassing typical levels for an individual’s age.
Neurologically, ADHD is linked to disturbances in the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for executive functions such as attention control, decision-making, and impulse regulation. These disturbances encompass neurotransmitter imbalances, notably dopamine and norepinephrine, crucial for modulating attention and behavior.
The intricate interplay of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors contributes to the origins of ADHD.
Adult ADHD vs ADD
ADHD and ADD represent distinct forms of attention deficit disorders, yet they share many common symptoms and features. ADHD involves challenges in maintaining focus and regulating impulsive behaviors. On the other hand, ADD is characterized by difficulty sustaining attention and managing impulses without the hyperactivity or restlessness typically associated with ADHD.
The Meaning of ADD To Most People
ADD is frequently regarded as primarily an “inattentive” disorder, suggesting that individuals with ADD can concentrate on tasks of interest, unlike those with ADHD, who may struggle to focus regardless of the task’s appeal. Additionally, individuals with ADD tend to be more composed and may encounter challenges in completing tasks, projects, or maintaining organization. In contrast, individuals with ADHD may be more susceptible to outbursts and engaging in risky behavior.
ADD vs ADHD Etiologic Theories
Neurobiological factors seem to contribute to the development of ADD. Investigations involving twins and adoptions provide compelling evidence of a genetic connection, with approximately 20% of parents of children with ADD experiencing the condition themselves. Individuals with ADD may encounter challenges in the prefrontal cortex, potentially influencing levels of dopamine and noradrenaline, along with structural alterations in the striatum and the cortex.
ADHD vs ADD Symptoms
ADD is a subtype of ADHD distinguished by challenges in paying attention and controlling impulses, notably lacking the hyperactivity typically associated with ADHD.
Individuals with ADD might require assistance in focusing on details, adhering to instructions, and maintaining organization, but they generally do not display excessive activity or impulsiveness.
In contrast, ADHD is characterized by a combination of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. People with ADHD may encounter difficulties in paying attention, following instructions, and staying organized, coupled with heightened activity and impulsivity.
Both ADHD and ADD in adults are thought to stem from a blend of genetic and environmental factors affecting individuals across all age groups. Treatment options for both conditions encompass medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments.
ADD vs ADHD Adults Treatment
In the treatment of adults dealing with ADD or ADHD, it is vital to take into account their unique needs and circumstances. Tailored care beyond conventional mental health treatment programs is often necessary for individuals with ADD or ADHD.
A specialized facility addressing ADD or ADHD should comprehend how symptoms impact an adult’s ability to navigate tasks and other facets of recovery. Therapies provided at these centers ought to concentrate on assisting adults in managing their symptoms while concurrently addressing underlying issues like depression or anxiety. The program should also incorporate strategies to empower individuals in effectively managing their attention deficits over the long term.
While there is no cure for either disorder, medication and behavioral therapies can alleviate symptoms and enhance functionality. Cognitive behavioral therapy and lifestyle adjustments such as increased physical activity and improved sleep habits can contribute to symptom management.
ADD vs ADHD Comorbidity
Half of individuals with ADD experience coexisting psychiatric conditions: 19% to 37% contend with mood disorders like depression, bipolar affective disorders, and dysthymia, 25% to 50% grapple with anxiety disorders, 32% to 53% face challenges related to addiction, and 10% to 28% exhibit symptoms of personality disorders.
If you’re seeking assistance with your rehab journey, reach out to a We Level Up Texas treatment professional today—your call is free and confidential.

Get Your Life Back
Find Hope & Recovery. Get Safe Comfortable Detox, Addiction Rehab & Dual Diagnosis High-Quality Care.
FREE Addiction Hotline – Call 24/7ADD vs ADHD Disorders Statistics
When the American Psychiatric Association released a revised edition in 1987, they combined these two subtypes into one condition, ADHD. Adults can have ADHD, too. Nearly 2.6 percent of adults globally have persistent ADHD from childhood, while about 6.7 percent of adults have symptoms of adult ADHD.
8.7 Million
In 2019, the number of visits to medical offices with attention deficit disorder as the primary diagnosis was 8.7 million.
Source: NIMH
30%
Inattentive ADHD, also known as ADHD predominantly inattentive presentation, is estimated to affect around 25% to 30% of individuals diagnosed with ADHD.
Source: NIMH
1 in 5
In 2020, nearly one in five US adults had a mental illness, including ADHD.
Source: NIMH
Top 5 Signs of ADHD in Adults
ADHD is not confined to childhood; it can endure into adulthood, albeit with potentially distinct manifestations. Numerous individuals with undiagnosed or untreated ADHD grapple with symptoms that significantly influence their adult lives, affecting areas such as work, relationships, and overall functioning.
In adults, ADHD may manifest more subtly, leading to potential misinterpretation as another mental health condition, thereby complicating the diagnosis. Identifying the distinctions between ADHD and ADD is an initial stride toward effecting positive changes. Armed with accurate information, individuals are empowered to seek professional assistance, overcome challenges, and foster personal growth.
1. Difficulty Focusing
Adults with ADHD may struggle to regulate their focus and encounter challenges in concentration. Observable manifestations may include:
- Easy distractibility.
- Frequent daydreaming.
- Zoning out during conversations.
- Overlooking instructions and details.
- A need to complete projects or tasks on time.
Another noteworthy symptom of ADHD in adults is the inclination to hyperfocus on projects that evoke excitement and interest. Maintaining focus on other essential tasks or interactions may become difficult during this state.
2. Misplacing Items
Individuals with ADHD may encounter difficulty storing, organizing, or keeping track of their belongings. This can manifest as:
- Misplacing everyday items (e.g., car keys or wallet) while the mind is on autopilot.
- Losing track of the location of an item after a moment of inattention.
- Frequent retracing of steps to locate lost items.
- Storing things in incorrect places (e.g., work papers in the car, dirty dishes in the bedroom).
3. Always Running Late
Frequent tardiness is a common challenge for individuals with ADHD, stemming from difficulties in time management. Reasons for being consistently late for appointments, meetings, or social plans often include:
- Difficulty locating necessary items (such as car keys, wallet, or meeting notes).
- Forgetfulness regarding dates and times.
- Underestimating the time required to finish projects or tasks.
- Getting easily distracted while preparing for an appointment or event.

4. Risky Behaviors
Studies indicate that adults with ADHD are more prone to engaging in risk-taking behavior. Taking the initiative to seek help and support can diminish the likelihood of involvement in these activities. Such behaviors may include:
- Initiating arguments or fights.
- Excessive spending.
- Reckless driving.
- Substance use (alcohol or drugs).
- Making risky decisions related to sexual activities (e.g., unprotected sex).
- Engaging in gambling.
- Impulsive eating.
5. Lack of Listening Skills
Navigating social interactions can be challenging for individuals with ADHD, who may encounter difficulties in the following areas:
- Waiting for their turn to speak.
- Staying on topic.
- Keeping track of the conversation.
- Employing non-verbal cues to indicate active listening.
- Speaking too quickly.
- Excessive talking.
- Blurting out words that may make others uncomfortable.
- Difficulty in interpreting other people’s body language.
ADD vs ADHD Infographic
ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity symptoms. At the same time, ADD (attention deficit disorder) is an outdated term previously used to describe the inattentive subtype of ADHD.
Embed the below “ADD vs ADHD” Infographic to your website. The We Level Up FL mental treatment center team provides this infographic. To use the below infographics, you agree to link back and attribute its source and owner at https://welevelupfl.com/behavioral-health/add-vs-adhd/
ADD vs ADHD Infographic image link: https://welevelupfl.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/ADD-vs-ADHD-1030×1030.jpg
How is ADHD Diagnosed?
Researchers are actively investigating the causes and risk factors of ADHD to develop more effective strategies for managing and minimizing the likelihood of an individual developing ADHD.
While the precise reasons and risk factors for ADHD remain unclear, current research emphasizes the substantial influence of genetics. Recent studies establish a connection between genetic factors and ADHD.
In addition to genetics, scientists are exploring other potential causes and risk factors, such as:
- Brain injury.
- Exposure to environmental risks (e.g., lead) during pregnancy or young age.
- Alcohol and tobacco use during pregnancy.
- Premature delivery.
- Low birth weight.
Research does not substantiate commonly held beliefs that ADHD is triggered by factors such as excessive sugar consumption, prolonged television watching, parenting practices, or socio-environmental elements like poverty or family disarray. While certain factors, including these, might exacerbate symptoms, particularly in specific individuals, the evidence is not robust enough to designate them as primary causes of ADHD.
Determining whether an individual has ADHD is a multi-step process. The symptoms of various other conditions, such as anxiety, depression, sleep disorders, and specific learning difficulties, may overlap with those of ADHD, making it impossible to diagnose with a single test. A medical examination, which encompasses hearing and vision assessments, is one stage in eliminating other conditions presenting similar symptoms to ADHD. The diagnosis of ADHD typically involves using a checklist to assess symptoms and gathering background information from parents, teachers, and occasionally the patient themselves.
ADD vs ADHD Facilities
ADD and ADHD treatment centers should prioritize supporting the families of individuals with these disorders. Family-focused therapies, such as couples therapy and family counseling, can aid individuals and their loved ones cultivate healthy communication strategies, fostering long-term recovery success.
An ADD vs ADHD rehabilitation center must also impart education about mental health and its impact on both the affected individual and their family. Armed with this knowledge, families can better understand the individual’s experiences and learn how to provide optimal support during and after treatment.
Mental health rehabilitation centers explicitly geared toward adults with ADD vs ADHD can offer comprehensive care, providing individuals with the best chances of reclaiming a fulfilling life. These facilities should boast experienced staff well-versed in ADHD treatment and mental health, equipped to address various symptoms, signs, and comorbidities.
Opting for an inpatient program for ADHD treatment offers several advantages, including:
- Structured Environment: Inpatient rehab establishes a highly structured setting, aiding individuals with ADHD in establishing routines and refining time management skills.
- Intensive Therapy: Inpatient programs provide concentrated therapy and counseling sessions, allowing for focused attention on addressing ADHD symptoms and associated challenges.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Inpatient rehabilitation often involves a diverse team of specialists, including psychiatrists, psychologists, occupational therapists, and social workers, contributing to a holistic approach to treatment.
ADD vs ADHD Medication
ADHD is frequently managed with one of three categories of medication—psychostimulants, antidepressants, or non-stimulant drugs.
Individuals with inattentive ADD may find relief from anxiety and ADD medication to enhance focus and maintain attention.
- Psychostimulants: These drugs impact neurotransmitters in the brain, potentially providing heightened energy and attentiveness for individuals with ADD and anxiety. Extended-release formulations are often preferred over immediate-release ones. Examples of psychostimulants include amphetamines like Adderall and methylphenidates such as Ritalin and Concerta.
- Antidepressants: By influencing neurotransmitters, antidepressants can contribute to mood and attention improvement for those dealing with adult ADD and anxiety. Wellbutrin (bupropion) and Effexor (venlafaxine) are common antidepressants recommended for ADHD’s inattentive symptoms.
- Non-stimulant drugs: In cases where stimulant side effects are undesirable, non-stimulant ADD medications may be advantageous. Medications for anxiety or ADD, such as Strattera (atomoxetine) and Intuniv (guanfacine), work by affecting the neurotransmitter norepinephrine, potentially regulating emotions and enhancing focus on specific tasks.
Like any medication, psychostimulants, antidepressants, and non-stimulants may lead to common side effects such as dizziness, loss of appetite, and upset stomach. It is crucial to consult with your doctor if you or someone you care about is experiencing any unusual symptoms.
Behavioral Therapy for ADHD
Whether or not patients opt for medication as a treatment, most psychologists recommend developing a behavior intervention plan to teach adaptive behavior skills and diminish off-task and inattentive behaviors. This often involves a combination of various methods:
- Behavior Therapy: A therapist typically engages with you and your loved one with ADHD. Sessions may involve facilitating conversations or providing activities to help express feelings. Family therapy may be recommended for all family members to learn healthy ways to manage the condition.
- Parent Training in Behavior Management: This involves learning strategies like talk therapy to allow your loved one to freely express feelings and adopt healthy coping mechanisms for challenging emotions.
- Behavioral Interventions at School: Your loved one may qualify for extra assistance under the Individuals With Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) or Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973. Accommodations may include spare time on tests, additional breaks, environmental changes, positive reinforcement, and customized assignments.
- Behavioral Peer Interventions: A therapist or trained professional may lead a group in activities that teach constructive peer interactions. Skills like conversation, handling teasing, and making friends are introduced, with reinforcement of these lessons at home and school by loved ones.
Best ADD Medication for Adults with Anxiety
The symptoms of ADHD and ADD share similarities but represent distinct conditions. Individuals with ADD do not experience hyperactivity; their primary challenge lies in maintaining attention. Although current diagnostic criteria do not delineate ADD as a separate condition, grouping its symptoms under inattentive ADHD, individuals with both ADHD and ADD can encounter difficulties throughout their lives, from childhood to adulthood.
Obtaining an accurate diagnosis may take time, but doctors can assist individuals through lifestyle changes and potentially recommend medication once achieved. If someone exhibits symptoms hindering academic or work progress or disrupting relationships, seeking medical help is advisable.
The benefits of ADHD medication can vary, and decisions about medication should be collaborative with a healthcare professional. Benefits include:
- Improved Focus.
- Reduced Impulsivity.
- Enhanced Executive Functioning.
- Better School/Work Performance.
- Positive Social Interactions.
- Boosted Self-Esteem.
- Decreased Anxiety.
- Improved Quality of Life.
- Easier Learning.
- Effective Coping.
Get Help. Get Better. Get Your Life Back.
Searching for Accredited Drug and Alcohol Rehab Centers Near You? We Level Up Texas Is Opening Soon!
Even if you have failed previously and relapsed, or are in the middle of a difficult crisis, we stand ready to support you. Our trusted behavioral health specialists will not give up on you. When you feel ready or just want someone to speak to about therapy alternatives to change your life call us. Even if we cannot assist you, we will lead you to wherever you can get support. There is no obligation. Call our network hotline today.
FREE Addiction Hotline – Call 24/7The Difference Between ADD vs ADHD Video
The Difference Between ADD vs ADHD Video Script
Welcome to the We Level Up treatment center video series. In today’s video we will discuss
ADD vs ADHD Symptoms
ADD (attention deficit disorder) vs ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder)
are two terms that are often confused.
ADHD symptoms include
hyperactivity,
impulsivity,
and inattention.
In contrast, ADD symptoms of inattention are related to an outdated term that refers to a subtype of ADHD with inattention symptoms.
It’s essential to get an accurate diagnosis from a healthcare professional to receive the appropriate treatment for ADHD.
By examining these distinct types, we gain insights into how individuals’ attention and cognitive functions may vary,
contributing to a more nuanced comprehension of this neurodevelopmental condition.
The term “ADD” is no longer used by healthcare professionals.
Instead, the condition is now divided into three subtypes of ADHD.
Each subtype represents a different pattern of symptoms and behavior.
Predominantly Inattentive Type ADHD
The DSM-5 (a manual for mental disorders) gives the rules for diagnosing different mental conditions, like ADHD.
When it comes to this type of ADHD (which used to be called ADD), the signs of hyperactivity are not there.
But people with it may still show these signs:
Can’t organize tasks or activities.
You can be easily distracted from the job you are given.
You often forget everyday activities.
You always lose things that you need to complete work.
You avoid, dislike, or postpone happenings that are not interesting to you.
You always lose your concentration on projects, chores, or duties in the workplace or office.
You can’t follow clear directions.
You seem not to be listening.
You often make careless mistakes.
You have trouble focusing on tasks or social activities.
In the ADD vs ADHD DSM 5, ADHD includes both the inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive presentations, replacing the previously used term ADD.
Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive Type ADHD
Individuals with hyperactive-impulsive type ADHD will have the following signs. They will show signs of:
Being constantly “on the go.”
Squirming in their seat, fidgeting with objects on their desk, or tapping their hands or feet.
Regularly leaving their seat at inappropriate times, such as during work meetings, classes, or presentations.
Talking excessively.
Having trouble waiting their turn.
Interrupting others in conversation or intruding on activities.
Blurting out answers before a question is finished.
ADHD Combined Type
This, the most common type of ADHD, is characterized by impulsive and hyperactive behaviors, inattention, and distractibility.
Furthermore, the following conditions must be met:
Several inattentive or hyperactive-impulsive symptoms are present.
Several symptoms are present in two or more settings.
such as at home, school, or work; with friends or relatives; or in other activities
There is clear evidence that the symptoms interfere with or reduce the quality of social, school, or work functioning.
The symptoms are not better explained by another mental disorder (such as mood, anxiety, dissociative, or personality disorders). The symptoms do not happen only during schizophrenia or another psychotic disorder.
How is ADHD Diagnosed?
Scientists are studying causes and ADHD risk factors to find better ways to manage and reduce the chances of a person having ADHD.
The reasons and risk factors for ADHD are unknown, but current research shows that genetics plays a significant role. Recent studies link genetic factors with ADHD.
In addition to genetics, scientists are studying other possible causes and risk factors, including the following:
Brain injury.
Exposure to environmental risks (e.g., lead) during pregnancy or young age.
Alcohol and tobacco use during pregnancy.
Premature delivery.
Low birth weight.
Research does not support the popularly held views that ADHD is caused by:
overeating sugar,
watching too much television,
parenting,
or social and environmental factors such as poverty or family chaos.
Of course, many things, including these, might worsen symptoms, especially in certain people.
But the evidence is not strong enough to conclude that they are the leading causes of ADHD.
Deciding if an individual has ADHD is a process with several steps.
The symptoms of many other conditions, including anxiety,
depression,
sleep issues,
and specific learning difficulties,
might be similar to those of ADHD, which cannot be diagnosed with a single test.
A medical checkup, which includes hearing and vision testing, is one stage in the procedure to rule out other conditions with symptoms similar to ADHD.
A checklist for grading ADHD symptoms and obtaining background information from parents, teachers, and occasionally the patient themselves are typically used to diagnose ADHD.
ADD vs ADHD Facilities
ADD vs ADHD treatment facilities need to support the family of those with ADD or ADHD disorders.
Family-oriented therapies, such as couples therapy and family counseling,
can help individuals and their loved ones develop healthy communication strategies that will lead to long-term recovery success.
It is also essential for an ADD vs ADHD rehab center to provide education about mental health and its effects on both the individual and their family members.
With this information, families can better understand what the individual is going through and how they can best support them during treatment and afterward.
By offering comprehensive care tailored specifically for adults with ADD vs ADHD, mental health rehab centers can give individuals the best chance at achieving living fully again.
he facility should have experienced staff knowledgeable about ADHD treatment and mental illness so they can adequately address different signs and symptoms and comorbidities.
The benefits of getting into an inpatient program for ADHD treatment include the following:
Structured Environment
Inpatient rehab provides a highly structured setting that helps individuals with ADHD establish routines and develop better time management skills.
Intensive Therapy
Inpatient programs offer intensive therapy and counseling sessions, allowing for focused attention on addressing ADHD symptoms and related challenges.
Multidisciplinary Approach
Inpatient rehab often involves a team of specialists, including psychiatrists, psychologists, occupational therapists, and social workers, providing a holistic approach to treatment.
We Level Up FL offers an ADHD treatment program at our mental health treatment center in Florida.
Here, clients participate in clinical and experiential therapies as part of our comprehensive curriculum.
If your loved one is struggling with their ADHD diagnosis, we can help them understand their disorder and teach them the skills they need to reach their full potential.
Please call We Level Up immediately to learn how our detox and addiction treatment program will help you overcome your Pink Cocaine Addiction.
That’s it for today
Please subscribe and hit the notification bell.
Like, share and comment.
We would love your feedback.
Have a great day.
We Level Up TX ADHD Treatment Center
Managing adult ADHD and ADD typically entails a blend of medication and therapy sessions. The predominant challenge may influence the approach. For instance, addressing ADHD-related stress as a priority may alleviate a contributing factor to co-occurring mental health conditions, such as depression. The choice of where to begin in the treatment process depends on identifying the primary issue causing distress.

ADHD is commonly addressed with stimulant medications that enhance brain chemicals associated with focus and cognitive function. While these medications can alleviate symptoms during school or work, they may also reduce appetite, headaches, or sleep disturbances.
Certain ADHD medications, classified as non-stimulants, offer alternatives with different side effect profiles, although they may not produce immediate effects. Combining stimulant and non-stimulant drugs is a strategy your doctor might employ.
Coping with symptoms of ADD vs ADHD in adults poses challenges, but effective management is possible. Mental health professionals may prescribe stimulant and antidepressant medications alongside recommending counseling or other therapeutic interventions.
Our mental health treatment center in Texas, We Level Up TX provides an ADHD treatment program. Clients engage in a holistic curriculum that includes clinical and experiential therapies. If your loved one is grappling with an ADHD diagnosis, we are here to assist them in comprehending their disorder and equipping them with the necessary skills to achieve their full potential.
Opening Soon! First-Class Facilities & Amenities
World-Class High-Quality Addiction & Mental Health Rehabilitation Treatment
Coming Soon! Rehab Centers TourRenowned Addiction Centers. Serene Private Facilities. Inpatient Rehab Programs Vary.
FREE Addiction Hotline – Call 24/7Proven recovery success experience, backed by a Team with History of:
- 15+ Years Experience
- 100s of 5-Star Reviews
- 10K+ Recovery Successes
- Low Patient to Therapist Ratio
- Onsite Medical Detox Center
- Comprehensive Dual-Diagnosis Treatment
- Complimentary Family & Alumni Programs
- Coaching, Recovery & Personal Development Events
Top 3 Add vs Anxiety in Adults FAQs
-
Does ADD cause anxiety?
Yes. Anxiety vs ADD, adults with ADHD or ADD lead anxious lives. The nature of ADHD often makes day-to-day life stressful, making situations and environments fraught with tension.
-
Can ADD cause anxiety?
Yes. ADD or ADHD, and anxiety disorders frequently occur together. Both of these diseases may coexist, or ADHD may influence the emergence of an anxiety illness. People with ADHD often also suffer from other mental health issues.
-
Can anxiety cause ADD?
ADHD and ADD symptoms do often resemble and coincide with those of other conditions like depression, anxiety, or bipolar disorder, leading to misdiagnosis but also insufficient diagnosis when unrecognized comorbidities exist.
Learn About Anxiety Disorder Facts & Anxiety Treatment Programs That Can Help You.
Is it ADHD? ADD or anxiety? ADHD and anxiety are inextricably linked. Anxiety disorder is the most prevalent comorbidity of ADHD, in part because the ADHD experience leads to a life filled with stress and concern. Anxiety disorders are an overall mental health condition. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, 31.1% of Americans have suffered from some anxiety disorder.
ADHD often coexists with anxiety, creating a complex interplay between these conditions. Individuals with ADHD may experience heightened anxiety levels due to challenges in focusing and impulsivity, while anxiety can exacerbate ADHD symptoms, leading to difficulties in concentration and self-regulation. Recognizing and addressing this dual relationship is crucial for effective treatment and management.
Get a free rehab insurance check without any obligation. The result can help you explore several treatment options.
Start a New Life
Begin with a free call to an addiction & behavioral health treatment advisor. Learn more about our dual-diagnosis programs. The We Level Up treatment center network delivers recovery programs that vary by each treatment facility. Call to learn more.
- Personalized Care
- Caring Accountable Staff
- World-class Amenities
- Licensed & Accredited
- Renowned w/ 100s 5-Star Reviews
We’ll Call You
Sources
[1] What is ADHD? | CDC Examining ADD vs ADHD
[2] NIMH » Mental Illness (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD Review
[3] NIMH » Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) (nih.gov)
[4] Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD Adults Review.
[5] ADHD: Reviewing the Causes and Evaluating Solutions – PMC (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD in Adults Causes.
[6] What is mental health? Evidence towards a new definition from a mixed methods multidisciplinary, international survey – PMC (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD Symptoms
[7] COMMON MENTAL HEALTH DISORDERS – Common Mental Health Disorders – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD in Female Adults
[8] About Mental Health (cdc.gov) ADD vs ADHD Related Topics.
[9] Information about Mental Illness and the Brain – NIH Curriculum Supplement Series – NCBI Bookshelf
[10] Effective Mood and Personality Disorder Treatment (welevelupnj.com)






